N
| = the number of individual values in the distribution.
Xi
| This is a symbol referring to the N individual values of your distribution in the abstract. Each value in the distribution is spoken of as a variate instance of the variable X. Thus, the first value in the distribution would be X1; the second would be X2; and so on to the last value, XN.
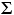
| This symbol (upper-case Greek letter 'sigma') does not represent a numerical value, but rather, like "+" and "—", a mathematical operation that is to be performed upon certain designated numerical values. It is a computational signpost saying "calculate the sum of these values"; hence its conventional name, the summation sign. Thus for a distribution of size N = 4, consisting of the values 6, 9, 12, and 15, the expression 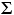 Xi would be equivalent to 6+9+12+15 = 42. Xi would be equivalent to 6+9+12+15 = 42.
M
| We will use the bold-face letter M to represent the arithmétic mean of a distribution. Thus MX would be the mean of a set of X values, MY would be the mean of a set of Y values, and so on. [Note that hardcopy statistics textbooks will often represent the mean of X (Y, Z, etc.) by writing the letter X (Y, Z, etc.) with a horizontal bar over it.]
| | | |