| Psychology 105 | Richard Lowry ©1999-2002 |
| "How often things occur by the merest chance." — |
| Click! |
| r[population]=0 |
|
Phase I. Toss the dice together 5 times, recording for each toss the number that comes up for X and the number that comes up for Y. The possibilities are of course 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 for each of the two dice on each toss. Then calculate the correlation coefficient for your 5 XiYi pairs. Record this calculated value of r, and then repeat the whole operation again and again, for as many times as you have the energy and patience If you feel foolish while doing it, keep reminding yourself that you are not merely tossing dice. What you are really doing is collecting a multiplicity of random bivariate samples, each of size Phase II. Now do the same thing as in Phase I, but this time make your samples of |
9.1a | 9.1b |
9.2a | 9.2b |
9.3a | 9.3b |
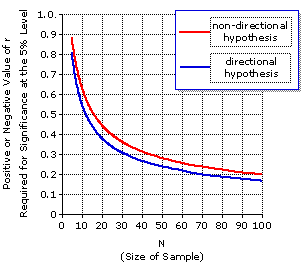
For any particular sample size, an observed value of r is regarded as statistically significant at the 5% level if and only if its distance from zero is equal to or greater than the distance of the tabled value of r. Thus, for a sample of size |
| Hypothesis | Hypothesis|
| Directional | Non- | Directional
| Directional | Non- | Directional N | ± r | ± r | N | ± r | ± r | 5 | 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
0.81 | 0.73 0.67 0.62 0.58 0.55 0.52 0.50 0.48 0.46 0.44 0.43 0.41 0.40
0.88 | 0.81 0.75 0.71 0.67 0.63 0.60 0.58 0.55 0.53 0.51 0.50 0.48 0.47
19 | 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
0.39 | 0.38 0.37 0.36 0.35 0.34 0.34 0.33 0.32 0.32 0.31 0.31 0.30 0.30
0.46 | 0.44 0.43 0.42 0.41 0.40 0.40 0.39 0.38 0.37 0.37 0.36 0.36 0.35 | |||||
POSITIVE DIRECTIONAL HYPOTHESIS: the relationship between X and Y in the general population is positive (the more of X, the more of Y), hence this particular sample of XiYi pairs will show a positive correlation;|
| or
|
| NEGATIVE DIRECTIONAL HYPOTHESIS: the relationship between X and Y in the general population is negative (the more of X, the less of Y), hence this particular sample of XiYi pairs will show a negative correlation. | |
| NON-DIRECTIONAL HYPOTHESIS: the relationship between X and Y in the general population is something other than zero, hence this particular sample of XiYi pairs will show a non-zero correlation, either positive or negative, though we have no basis for predicting just which of these it will be. |